VASCULAR DISEASE
Vascular disease is a condition that affects the arteries and/or veins. Most often, vascular disease affects blood flow, either by blocking or weakening blood vessels, or by damaging the valves that are found in veins. Organs and other body structures may be damaged by vascular disease as a result of decreased or completely blocked blood flow. Vascular disease includes:
Peripheral Artery Disease: Disease in blood vessels outside your brain and heart.
Carotid Artery Disease: Blockages or damage to the arteries supplying the brain.
Blood Clots: Blood becomes a solid mass, blocking the normal flow of blood in the vessels.
Aneurysm: Bulges in the wall of a blood vessel.
Venous Disease: Valves that regulate the one-way flow of blood in the veins become diseased and unable to function properly, leading to blood flow in both directions.
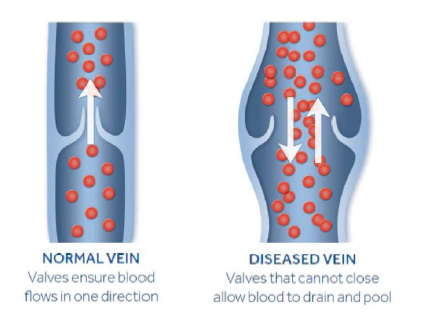
Causes of vascular disease include:
Embolus/thrombus: A blood vessel may be blocked by an embolus (a tiny mass of debris that moves through the bloodstream) or a thrombus (a blood clot).
Inflammation: In general, inflammation of blood vessels is referred to as vasculitis, which includes a range of disorders. Inflammation may lead to narrowing and/or blockage of blood vessels.
Trauma/injury: Trauma or injury involving the blood vessels may lead to inflammation or infection, which can damage the blood vessels and lead to narrowing and/or blockage.
Atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis is a disease in which a waxy substance called plaque builds up on the inner lining of arteries. Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, fibrous tissue and calcium. When present, plaque may reduce or fully block the flow of oxygen-rich blood through arteries to the body’s vital organs and the limbs.
Symptoms of vascular disease vary by cause and site.
